相关的文件
- linux-4.4.23/include/linux/init.h
- linux-4.4.23/init/main.c
- linux-4.4.23/arch/x86/kernel/vmlinux.lds.S
- linux-4.4.23/include/asm-generic/vmlinux.lds.h
本文中使用的vmlinux是由linux 4.4.23源码编译。
相关宏定义
相关代码如下:
/*
* Used for initialization calls..
*/
typedef int (*initcall_t)(void);
/* initcalls are now grouped by functionality into separate
* subsections. Ordering inside the subsections is determined
* by link order.
* For backwards compatibility, initcall() puts the call in
* the device init subsection.
*
* The `id' arg to __define_initcall() is needed so that multiple initcalls
* can point at the same handler without causing duplicate-symbol build errors.
*/
#define __define_initcall(fn, id) \
static initcall_t __initcall_##fn##id __used \
__attribute__((__section__(".initcall" #id ".init"))) = fn; \
LTO_REFERENCE_INITCALL(__initcall_##fn##id)
/*
* Early initcalls run before initializing SMP.
*
* Only for built-in code, not modules.
*/
#define early_initcall(fn) __define_initcall(fn, early)
/*
* A "pure" initcall has no dependencies on anything else, and purely
* initializes variables that couldn't be statically initialized.
*
* This only exists for built-in code, not for modules.
* Keep main.c:initcall_level_names[] in sync.
*/
#define pure_initcall(fn) __define_initcall(fn, 0)
#define core_initcall(fn) __define_initcall(fn, 1)
#define core_initcall_sync(fn) __define_initcall(fn, 1s)
#define postcore_initcall(fn) __define_initcall(fn, 2)
#define postcore_initcall_sync(fn) __define_initcall(fn, 2s)
#define arch_initcall(fn) __define_initcall(fn, 3)
#define arch_initcall_sync(fn) __define_initcall(fn, 3s)
#define subsys_initcall(fn) __define_initcall(fn, 4)
#define subsys_initcall_sync(fn) __define_initcall(fn, 4s)
#define fs_initcall(fn) __define_initcall(fn, 5)
#define fs_initcall_sync(fn) __define_initcall(fn, 5s)
#define rootfs_initcall(fn) __define_initcall(fn, rootfs)
#define device_initcall(fn) __define_initcall(fn, 6)
#define device_initcall_sync(fn) __define_initcall(fn, 6s)
#define late_initcall(fn) __define_initcall(fn, 7)
#define late_initcall_sync(fn) __define_initcall(fn, 7s)
#define __initcall(fn) device_initcall(fn)
workqueue.c中
early_initcall(init_workqueues);
扩展开来就是
static initcall_t __initcall_init_workqueuesearly __used\
__attribute__((__section__(".initcallearly.init"))) = init_workqueues; \
__initcall_init_workqueuesearly 是一个函数指针,指向init_workqueues; 该变量被链接到名为 .initcallearly.init 的 section 中。
linux内核的initcall是分等级的,从init.h中可以看到一共分为17个等级(实际上后接sync的的7个等级是没有用到的)。 优先级从上到下越来越低(early > 0 > 1 > 1s > … > 7s)。
链接生成linux内核文件
vmlinux.lds.S是x86内核的链接脚本。 该脚本中定义了内核文件中各个section的排列方式。
SECTIONS
{
. = __START_KERNEL; // __START_KERNEL = 0XFFFFFFFF81000000
phys_startup_64 = startup_64 - LOAD_OFFSET;
/* Text and read-only data */
.text : AT(ADDR(.text) - LOAD_OFFSET) {
......
} :text = 0x9090
......
X64_ALIGN_DEBUG_RODATA_BEGIN
RO_DATA(PAGE_SIZE)
X64_ALIGN_DEBUG_RODATA_END
/* Data */
.data : AT(ADDR(.data) - LOAD_OFFSET) {
......
} :data
......
/* Init code and data - will be freed after init */
. = ALIGN(PAGE_SIZE);
.init.begin : AT(ADDR(.init.begin) - LOAD_OFFSET) {
__init_begin = .; /* paired with __init_end */
}
INIT_TEXT_SECTION(PAGE_SIZE)
// initcall的数据段定义在这里
INIT_DATA_SECTION(16)
.x86_cpu_dev.init : AT(ADDR(.x86_cpu_dev.init) - LOAD_OFFSET) {
__x86_cpu_dev_start = .;
*(.x86_cpu_dev.init)
__x86_cpu_dev_end = .;
}
......
/*
* start address and size of operations which during runtime
* can be patched with virtualization friendly instructions or
* baremetal native ones. Think page table operations.
* Details in paravirt_types.h
*/
. = ALIGN(8);
.parainstructions : AT(ADDR(.parainstructions) - LOAD_OFFSET) {
__parainstructions = .;
*(.parainstructions)
__parainstructions_end = .;
}
/*
* struct alt_inst entries. From the header (alternative.h):
* "Alternative instructions for different CPU types or capabilities"
* Think locking instructions on spinlocks.
*/
. = ALIGN(8);
.altinstructions : AT(ADDR(.altinstructions) - LOAD_OFFSET) {
__alt_instructions = .;
*(.altinstructions)
__alt_instructions_end = .;
}
/*
* And here are the replacement instructions. The linker sticks
* them as binary blobs. The .altinstructions has enough data to
* get the address and the length of them to patch the kernel safely.
*/
.altinstr_replacement : AT(ADDR(.altinstr_replacement) - LOAD_OFFSET) {
*(.altinstr_replacement)
}
/*
* struct iommu_table_entry entries are injected in this section.
* It is an array of IOMMUs which during run time gets sorted depending
* on its dependency order. After rootfs_initcall is complete
* this section can be safely removed.
*/
.iommu_table : AT(ADDR(.iommu_table) - LOAD_OFFSET) {
__iommu_table = .;
*(.iommu_table)
__iommu_table_end = .;
}
. = ALIGN(8);
.apicdrivers : AT(ADDR(.apicdrivers) - LOAD_OFFSET) {
__apicdrivers = .;
*(.apicdrivers);
__apicdrivers_end = .;
}
. = ALIGN(8);
/*
* .exit.text is discard at runtime, not link time, to deal with
* references from .altinstructions and .eh_frame
*/
.exit.text : AT(ADDR(.exit.text) - LOAD_OFFSET) {
EXIT_TEXT
}
.exit.data : AT(ADDR(.exit.data) - LOAD_OFFSET) {
EXIT_DATA
}
#if !defined(CONFIG_X86_64) || !defined(CONFIG_SMP)
PERCPU_SECTION(INTERNODE_CACHE_BYTES)
#endif
. = ALIGN(PAGE_SIZE);
/* freed after init ends here */
.init.end : AT(ADDR(.init.end) - LOAD_OFFSET) {
__init_end = .;
}
/*
* smp_locks might be freed after init
* start/end must be page aligned
*/
. = ALIGN(PAGE_SIZE);
.smp_locks : AT(ADDR(.smp_locks) - LOAD_OFFSET) {
__smp_locks = .;
*(.smp_locks)
. = ALIGN(PAGE_SIZE);
__smp_locks_end = .;
}
......
/* BSS */
. = ALIGN(PAGE_SIZE);
.bss : AT(ADDR(.bss) - LOAD_OFFSET) {
__bss_start = .;
*(.bss..page_aligned)
*(.bss)
. = ALIGN(PAGE_SIZE);
__bss_stop = .;
}
. = ALIGN(PAGE_SIZE);
.brk : AT(ADDR(.brk) - LOAD_OFFSET) {
__brk_base = .;
. += 64 * 1024; /* 64k alignment slop space */
*(.brk_reservation) /* areas brk users have reserved */
__brk_limit = .;
}
_end = .;
......
}
其中INIT_DATA_SECTION 宏定义为:
#define INIT_DATA_SECTION(initsetup_align) \
.init.data : AT(ADDR(.init.data) - LOAD_OFFSET) { \
INIT_DATA \
INIT_SETUP(initsetup_align) \
// initcall defines \
INIT_CALLS \
CON_INITCALL \
SECURITY_INITCALL \
INIT_RAM_FS \
}
INIT_CALLS 宏定义为:
#define INIT_CALLS_LEVEL(level) \
VMLINUX_SYMBOL(__initcall##level##_start) = .; \
*(.initcall##level##.init) \
*(.initcall##level##s.init) \
#define INIT_CALLS \
VMLINUX_SYMBOL(__initcall_start) = .; \
*(.initcallearly.init) \
INIT_CALLS_LEVEL(0) \
INIT_CALLS_LEVEL(1) \
INIT_CALLS_LEVEL(2) \
INIT_CALLS_LEVEL(3) \
INIT_CALLS_LEVEL(4) \
INIT_CALLS_LEVEL(5) \
INIT_CALLS_LEVEL(rootfs) \
INIT_CALLS_LEVEL(6) \
INIT_CALLS_LEVEL(7) \
VMLINUX_SYMBOL(__initcall_end) = .;
从该ld脚本中可以知道
- linux内核文件中各个section的起始地址为0XFFFFFFFF81000000
- INIT_CALLS定义在.init.data section中
- INIT_CALLS的首尾定义分别为: __initcall_start(0xffffffff82082ef8) 和 __initcall_end(0xffffffff820842f0)
通过命令 readelf vmlinux 和 nm vmlinux 可以查看 __initcall_start 、 __initcall_end 和 __initcall_init_workqueuesearly等函数的地址信息
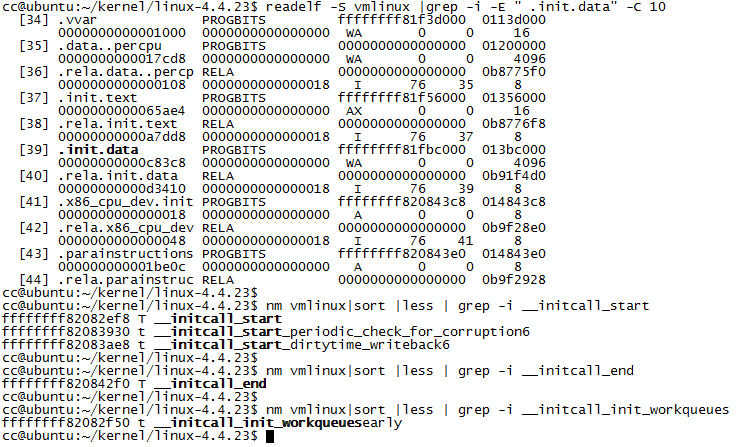
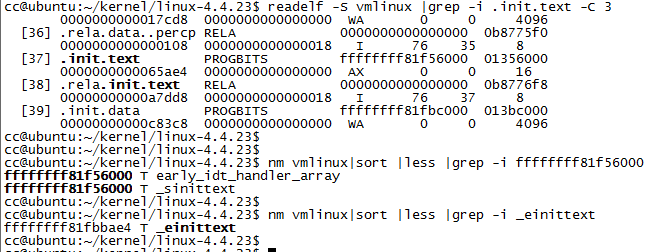
而init_workqueue函数的地址为, 该函数位于 .init.text section中,该section的起始和结束地址分别为: ffffffff81f56000 和 ffffffff81fbbae4。
内核执行initcalls系列函数
initcalls在内核初始化过程中调用关系如下
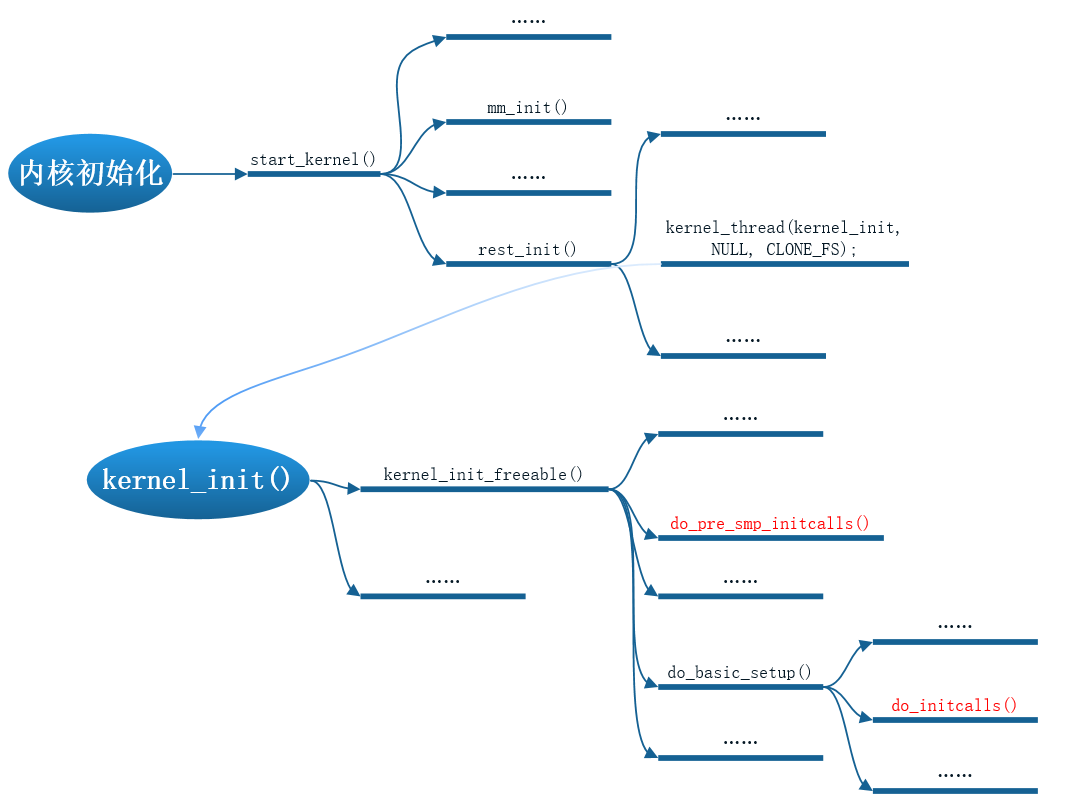
do_pre_smp_initcalls 为 initcall_early的调用函数
static void __init do_pre_smp_initcalls(void)
{
initcall_t *fn;
for (fn = __initcall_start; fn < __initcall0_start; fn++)
do_one_initcall(*fn);
}
__initcall_start对应的是initcall在.init.data section中的首地址, __initcall0_start为 level0的initcall在.init.data section中的首地址, 这两个地址之间的函数均为 __initcall_xxxearly 类型的initcall函数。
do_initcalls 为 initcall_levels的调用函数
static initcall_t *initcall_levels[] __initdata = {
__initcall0_start,
__initcall1_start,
__initcall2_start,
__initcall3_start,
__initcall4_start,
__initcall5_start,
__initcall6_start,
__initcall7_start,
__initcall_end,
};
static void __init do_initcall_level(int level)
{
initcall_t *fn;
strcpy(initcall_command_line, saved_command_line);
parse_args(initcall_level_names[level],
initcall_command_line, __start___param,
__stop___param - __start___param,
level, level,
NULL, &repair_env_string);
for (fn = initcall_levels[level]; fn < initcall_levels[level+1]; fn++)
do_one_initcall(*fn);
}
static void __init do_initcalls(void)
{
int level;
for (level = 0; level < ARRAY_SIZE(initcall_levels) - 1; level++)
do_initcall_level(level);
}
这两个函数中都调用了 do_one_initcall(*fn) 函数,其定义如下:
int __init_or_module do_one_initcall(initcall_t fn)
{
int count = preempt_count();
int ret;
char msgbuf[64];
if (initcall_blacklisted(fn))
return -EPERM;
if (initcall_debug)
ret = do_one_initcall_debug(fn);
else
ret = fn();
msgbuf[0] = 0;
if (preempt_count() != count) {
sprintf(msgbuf, "preemption imbalance ");
preempt_count_set(count);
}
if (irqs_disabled()) {
strlcat(msgbuf, "disabled interrupts ", sizeof(msgbuf));
local_irq_enable();
}
WARN(msgbuf[0], "initcall %pF returned with %s\n", fn, msgbuf);
return ret;
}